News detail
Working environment, types, requirements and development of refractory materials used in ladle
Introduction
Ladle is a necessary equipment for receiving molten steel and continuous casting. Since many types of steel need to be refined in the ladle, including argon blowing temperature adjustment, alloy composition fine-tuning, powder spray refining and continuous casting machine vacuum treatment, the working conditions of the ladle lining are getting worse and worse.
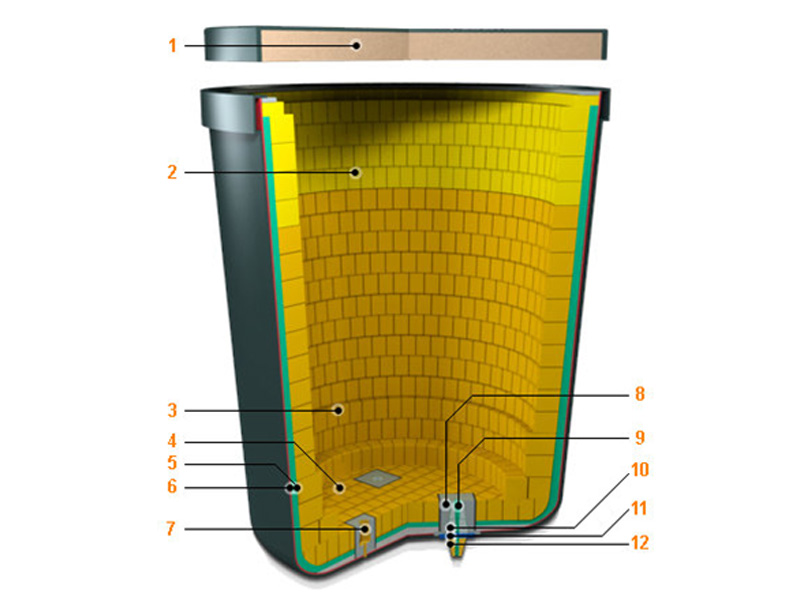
The refractory materials of the ladle lining are generally divided into four parts: insulation layer refractory materials, permanent layer refractory materials, working layer refractory materials, and functional refractory materials.
The insulation layer refractory materials play a role of insulation, and are generally lightweight insulation materials, such as: lightweight clay bricks, aluminum silicate fiberboards, lightweight coatings, lightweight porous castables, nano-reflective insulation boards, etc.

The permanent layer refractory materials are also called safety layer refractory materials. They mainly play an insurance role to prevent the molten steel that leaks through after the working layer refractory materials are damaged and burn the metal shell, ensuring the safety of use. The main materials of the permanent layer refractory materials are: high alumina bricks, aluminum-magnesium castables, high alumina castables, etc.

The working layer refractory material is in direct contact with the slag and molten steel in the ladle. It must be able to withstand the high temperature erosion of slag and the erosion of molten steel. The service life of the ladle is determined by the mechanical erosion of the molten steel on the working layer refractory material and the process level of this layer. The working layer refractory material has gone through different stages such as clay bricks, high alumina bricks, wax stone bricks, carbon-free, low-carbon, and special refractory materials.
Working environment of ladle refractory materials
The molten steel temperature is higher than that of the die-cast ladle.
The residence time of molten steel in the ladle is extended.
The ladle lining volatilizes itself under high temperature vacuum and withstands the stirring effect of molten steel.
The impact of the lining when receiving molten steel.
The erosion of the lining by molten slag.
Requirements for ladle refractory materials
High temperature resistance, able to withstand the long-term action of high temperature molten steel without melting and softening.
Resistant to heat shock, can withstand repeated loading and unloading of molten steel without cracking and peeling.
Resistant to slag corrosion, can withstand the erosion of slag and slag basicity changes on the lining.
Has sufficient high-temperature mechanical strength, can withstand the stirring and scouring of molten steel.
The lining has a certain degree of expansion. Under the action of high-temperature molten steel, the linings are in close contact and become a whole.
Selection conditions of ladle refractory materials
The working conditions of the ladle, such as tapping temperature, molten steel residence time, pouring steel type, whether refining treatment is performed, etc.
The position of the ladle refractory material in the ladle.
The basicity of slag.
The working conditions and economic ladle age of the steel plant’s ladle building, dismantling, and baking.
Economical efficiency.
Development
As the lining material of the ladle, the aluminum-magnesium refractory castable must have excellent resistance to structural peeling and corrosion resistance. However, since it must be used in an environment above 1600℃ for a long time, the vicinity of its working surface will be damaged due to over-sintering and slag penetration. The phenomenon of vitrification occurs, which makes it difficult to ensure its durability. Adding a certain amount of magnesium oxide fine powder in the process of batching can effectively improve some properties of alumina-magnesia spinel castables. Magnesium oxide in magnesia sand and alumina in the material will generate in-situ spinel at high temperature, thereby strengthening the internal structure of the material, improving slag resistance and inhibiting slag penetration. It has a good effect of using, thereby greatly extending the service life of the ladle. Due to the reaction of Al2O3 and MgO at high temperature to generate in-situ spinel, the sample becomes loose and has fine knots inside, so this kind of ladle has better durability.
With the development and application of synthetic magnesium aluminum spinel materials, carbon-containing refractory materials and the development and progress of low-cement, ultra-low-cement and cement-free refractory castable technology, many steelmaking containers have begun to use a new generation of alumina/magnesia/graphite refractory materials, among which the application on ladles is the most.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!