News detail
Selection of refractory materials for tertiary air ducts
The function of the tertiary air duct is to introduce the excess cooling air of the grate cooler into the preheater. It mainly bears the wear of high-speed high-temperature air. The air temperature of the tertiary air duct can reach 1200 degrees, so it also has to bear some thermal stress. In order to keep warm, the tertiary air duct should also be pasted with a layer of high-temperature calcium silicate board, and then the refractory bricks are laid.、
The refractory materials used in the tertiary air duct of the rotary kiln include high-strength alkali-resistant bricks, high-strength alkali-resistant castables, wear-resistant castables, wear-resistant castable prefabricated parts, calcium silicate boards, diatomite bricks and lightweight castables. The Y-shaped parts, elbows and closing valves in the tertiary air duct are severely damaged and have the most demanding use conditions. The main cause of damage to the refractory materials in this area is the erosion and wear caused by the high-temperature gas containing alkali, sulfur and chlorine and the alkali, sulfur and chlorine erosion carrying a large amount of dust, which makes the refractory materials prone to wear, looseness and peeling.
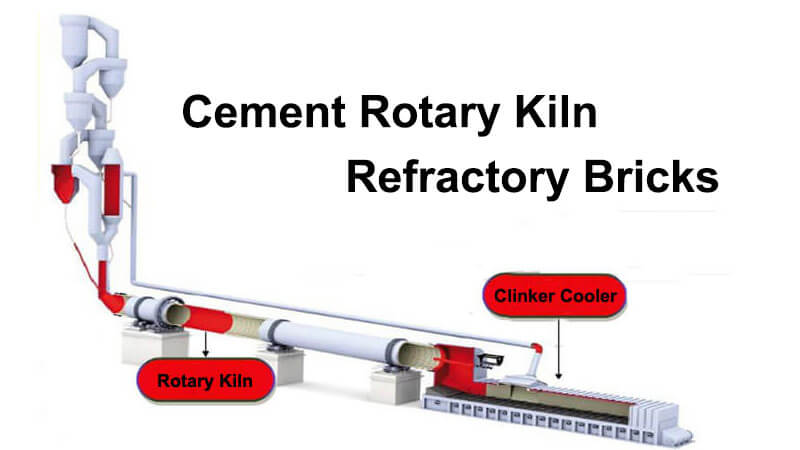
Although the tertiary air duct is in a static state for a long time, the wind speed in the duct can reach up to 20 meters/s. The scouring effect of the mixed cement clinker particles on the refractory bricks cannot be ignored. Therefore, the tertiary air duct is generally built with high-strength alkali-resistant bricks or 1550 silica-molybdenum bricks, and the service life is 2-3 years. The elbow of the tertiary air duct is built with steel fiber castables.
In the production process of cement kilns, the working conditions of the tertiary air duct are relatively complex. The gas with high temperature and high dust concentration circulates inside, and it also bears certain air flow scouring and temperature fluctuations. Therefore, it is very important to select refractory materials for tertiary air ducts reasonably, which is not only related to the service life of tertiary air ducts, but also affects the stable operation and production cost of cement kilns.
1. Analysis of tertiary air duct working conditions
The gas temperature in the tertiary air duct is usually around 800-1000℃, but under abnormal conditions, short-term over-temperature phenomena may occur. The gas contains a large amount of clinker dust, and the particles are relatively hard, which will have a strong scouring and wear effect on the lining of the air duct. Moreover, due to the intermittent production or working condition adjustment of cement kilns, the temperature and air flow velocity in the tertiary air duct will fluctuate, which further aggravates the thermal and mechanical stresses borne by the refractory materials.
2. Refractory material performance requirements
High temperature resistance: Able to withstand the normal operating temperature in the tertiary air duct and possible short-term over-temperature conditions, ensure that no softening, melting, etc. occur in a high temperature environment, and maintain its structural integrity and strength. For example, select materials with a refractoriness of not less than 1790℃ to cope with the high temperature challenges in actual operation.
Thermal shock resistance: In view of the temperature fluctuation, the refractory material should have good thermal shock resistance stability and should not crack or peel off during repeated rapid heating and cooling. Generally, the thermal shock resistance of the material is measured by testing the residual strength or crack extension of the material under a certain number of thermal cycles. For example, after 10 1100℃ water-cooled thermal shock tests, the strength loss of the material does not exceed a certain proportion.
Abrasion resistance: The ability to resist the erosion and wear of high-speed dust-laden airflow is the key. High-hardness and high-strength refractory materials can effectively reduce the thinning of the lining thickness and structural damage caused by dust erosion. The wear resistance is usually characterized by the amount of wear, and it is advisable to select materials with a wear amount lower than a specific value (such as ≤8cm³).
Chemical stability: In the complex chemical environment of the cement kiln, the refractory material should be in contact with components such as clinker dust and alkaline gas without chemical reaction to avoid performance degradation due to chemical erosion. For example, the material is required to have good alkali erosion resistance to prevent alkali metal oxides from penetrating into the material to cause structural damage and performance degradation.
3. Common types and characteristics of refractory materials
High-alumina refractory materials: have a high alumina content (Al₂O₃≥75%), good high temperature resistance, and can adapt to the high temperature environment in the tertiary air duct. It has high strength and can resist airflow scouring and thermal stress to a certain extent. However, it is relatively weak in thermal shock resistance and is prone to cracks when the temperature fluctuates greatly. However, by optimizing the production process and adding appropriate additives (such as zircon, etc.), its thermal shock resistance can be improved, making it more widely used in tertiary air ducts, especially in areas where the temperature is relatively stable and dust scouring is not too serious.

Silicon carbide refractory materials: with silicon carbide (SiC) as the main component, it has excellent high temperature resistance, high strength, high hardness and good thermal conductivity. It has outstanding wear resistance and can effectively resist the high-speed scouring of clinker dust. At the same time, it has good thermal shock resistance and performs well in the tertiary air duct environment with frequent temperature fluctuations. However, the cost of silicon carbide refractory materials is relatively high, and their anti-oxidation performance needs to be further improved. In actual use, anti-oxidation coatings are usually applied on their surfaces or used in combination with other antioxidants to enhance their anti-oxidation ability, and they are used in key parts with severe wear (such as duct elbows, straight sections with high air flow velocity, etc.) to improve the overall service life and cost performance.
![]()
Mullite refractory materials: Mullite (3Al₂O₃·2SiO₂) is a refractory material with good high temperature performance, thermal shock resistance and chemical stability as the main crystal phase. Its thermal expansion coefficient is low, and the thermal stress generated during temperature changes is small, which is conducive to resisting thermal shock damage. Although the wear resistance of mullite refractory materials is not as good as that of silicon carbide materials, they can meet the requirements under general tertiary duct working conditions, and the cost is relatively moderate. Therefore, in some non-critical parts of tertiary ducts or areas where the wear resistance requirements are not particularly stringent, mullite refractory materials are a more economical and practical choice.

4. Principles for the selection of refractory materials
Accurate matching according to working conditions: Detailed analysis of working parameters such as temperature distribution, air flow velocity, dust concentration and particle characteristics in the tertiary air duct to determine the differences in thermal stress, mechanical stress and chemical erosion degree of each part. For areas with high and stable temperature and less wear, high-aluminum refractory materials can be used first; in areas with large temperature fluctuations and severe erosion and wear, silicon carbide or improved high thermal shock resistance and high wear resistance refractory materials should be used; and for parts with relatively mild working conditions, mullite refractory materials may be more suitable, so as to achieve the optimal combination of refractory materials in different parts and reduce costs while ensuring performance.
Consider the overall cost-effectiveness: When selecting refractory materials, we should not only focus on the initial purchase cost of the materials, but also comprehensively consider factors such as their service life, maintenance cost and impact on cement kiln production stability. Although some high-performance refractory materials (such as silicon carbide) are expensive, their long life and good use effect may reduce the loss of production stoppage and maintenance costs caused by frequent replacement of linings. From the perspective of long-term operation, they have a higher cost-effectiveness. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a full life cycle cost analysis of different refractory material solutions and select the solution with the lowest total cost.
Pay attention to the quality stability and construction performance of the materials: Select refractory material suppliers with stable and reliable quality to ensure the performance consistency and reliability of the products, and avoid the construction quality and use effect of the tertiary air duct lining affected by material quality fluctuations. At the same time, the materials should have good construction performance, such as appropriate plasticity, masonry, drying and baking performance, etc., to facilitate on-site construction operations, ensure the masonry quality and integrity of the lining, reduce material loss and quality defects during construction, ensure that the refractory materials can give full play to their performance advantages during use, extend the service life of the tertiary air duct, and ensure the efficient and stable operation of the cement kiln.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!