News detail
Selection of refractory materials for rotary kiln mouth
The refractory materials for rotary kiln mouth mainly include various amorphous refractory materials with good high temperature performance, such as corundum castables, mullite castables, and andalusite castables. For cement kilns with small deformation at the kiln mouth of new kilns or kiln barrels, high wear-resistant silicon carbide bricks, wear-resistant high-alumina bricks and other shaped products can also be configured at the kiln mouth.
In modern industrial production, rotary kilns play an important role and are widely used in cement, metallurgy, chemical industry and other fields. As a key part of the rotary kiln system, the kiln mouth faces extremely harsh working conditions, which makes the selection of refractory materials the core link to ensure the efficient and stable operation of the rotary kiln.
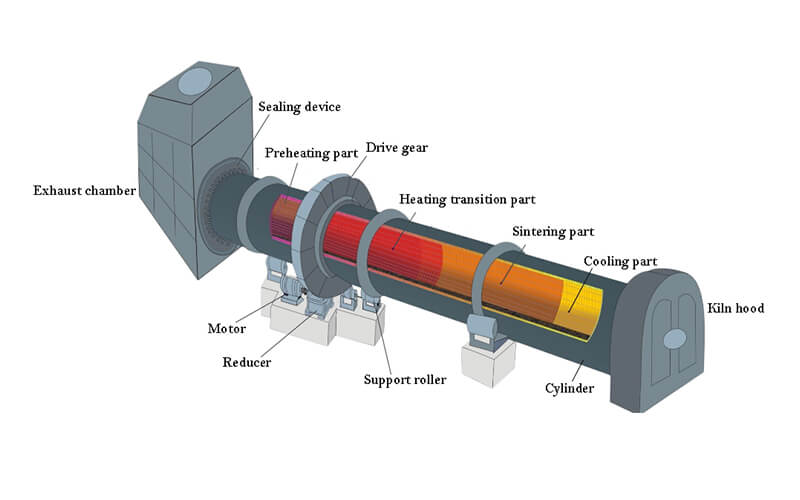
Characteristics of rotary kiln mouth working conditions
Severe temperature fluctuations
The kiln mouth is directly connected to the high-temperature environment inside the kiln, and the temperature can reach thousands of degrees Celsius during normal operation. In addition, during the process of opening and stopping the kiln and adjusting the working conditions, the temperature changes rapidly and with large amplitudes, and may rise and fall by hundreds of degrees in a short period of time, posing a huge challenge to the thermal stability of refractory materials.
Severe material scouring
The material continues to roll and push in the rotary kiln, and still has considerable kinetic energy when it reaches the kiln mouth, just like a high-speed flowing “sandpaper”, constantly rubbing and hitting the kiln mouth lining. This high-intensity material scouring day after day can easily cause the surface of the refractory material to wear and peel off.
Frequent chemical erosion
The raw material composition is complex, often containing various alkaline and acidic oxides, which react chemically with the refractory material at high temperature. For example, the alkaline substances contained in the clinker in cement production will corrode the refractory matrix, causing its structure to deteriorate and its strength to decrease, thereby affecting its service life.
Comparison of the performance of commonly used refractory materials
Clay Brick

The advantages are low price, certain heat insulation performance, and the ability to block the heat loss from the kiln to a certain extent. However, its refractoriness is relatively low, generally between 1650℃ and 1750℃, and its thermal shock resistance is poor. It is easy to crack under frequent temperature shocks at the kiln mouth, and its chemical erosion resistance is weak, making it difficult to meet the long-term use requirements of modern industrial rotary kiln mouths.
High alumina bricks

The alumina content is high, the refractoriness is increased to 1750℃ – 1850℃, the high temperature strength is good, and it can withstand a certain mechanical load. However, its thermal shock stability is not ideal. Facing the rapid cooling and heating conditions at the kiln mouth, it is easy to crack, which will bury the hidden danger of subsequent damage. However, compared with clay bricks, its corrosion resistance is enhanced.
Magnesium-aluminum spinel bricks

Made of magnesia and bauxite, the magnesia-alumina spinel structure gives it excellent resistance to alkaline erosion and can effectively resist the chemical attack of alkaline materials at the kiln mouth. It has good thermal shock stability, can adapt to frequent temperature fluctuations, and has high strength. The disadvantage is that the cost is relatively high and the production process requirements are also relatively strict.
Corundum mullite brick

It combines the high hardness and wear resistance of corundum with the excellent thermal shock stability of mullite. It has a refractoriness of over 1800℃ and strong chemical stability. It has excellent resistance to both material erosion and chemical corrosion. However, due to its high raw material cost and complex preparation process, it is expensive and its large-scale application is subject to certain restrictions.
Basis for refractory material selection
Specific working conditions of the kiln mouth
According to the industry in which the rotary kiln is located, the types of products produced, and the actual operating parameters, the temperature range, material characteristics, scouring and erosion degree faced by the kiln mouth can be accurately analyzed. For example, the rotary kiln in the metallurgical industry processes high-temperature metal ores, the kiln mouth temperature is high and the materials are highly corrosive, so corundum mullite bricks or magnesia-alumina spinel bricks may be given priority; while for some small cement plants, the kiln mouth working conditions are relatively mild, and high-alumina bricks may be able to meet the needs after reasonable maintenance.
Economic cost considerations
Not only should we pay attention to the initial purchase cost of refractory materials, but we should also comprehensively consider their service life, maintenance and replacement costs, and the impact on production efficiency. For example, although the purchase price of high-quality corundum mullite bricks is high, due to their long life and reduced number of shutdowns for maintenance, from a long-term operation perspective, the comprehensive cost may be lower than that of frequently replaced low-priced refractory materials.
Convenience of construction and maintenance
The selected refractory materials should be easy to install on site. For example, the brick design should conform to the kiln mouth structure, facilitate masonry, and reduce construction difficulty and construction period. At the same time, the later maintenance is simple and easy, such as easy local repair and replacement, which can reduce operation and maintenance costs and labor intensity.
Future development trend outlook
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, the refractory materials of rotary kiln mouth are expected to usher in new breakthroughs. On the one hand, new composite materials are developed to further optimize the balance of thermal shock stability, corrosion resistance and wear resistance, while reducing costs; on the other hand, with the help of intelligent manufacturing technology, customized production of refractory materials can be achieved, and the personalized needs of different kiln mouths can be accurately adapted to promote the development of the rotary kiln industry towards higher efficiency and lower energy consumption.
In short, the reasonable selection of refractory materials for rotary kiln mouths requires a comprehensive balance of various factors to maximize production efficiency and ensure the smooth progress of industrial production. In the future, it will continue to be optimized and upgraded with technological innovation.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!