News detail
Refractory materials for hot blast furnaces
The selection of refractory materials for hot blast furnaces is mainly determined by the hot blast temperature. When the hot blast temperature is lower than 900℃, clay bricks are generally used for masonry, and some of them have a service life of about 20 years; when the blast temperature is higher than 900℃, the furnace lining and checker bricks in the high-temperature parts are made of high-alumina bricks, mullite bricks, sillimanite bricks and silica bricks. However, the selection of refractory materials in different countries is also different.
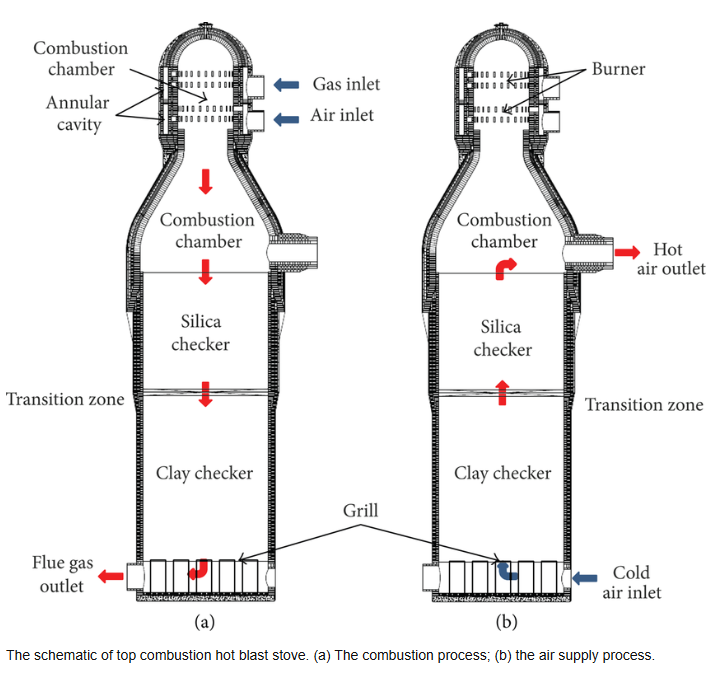
Japan’s large blast furnace hot blast furnace mainly adopts Koppers type. Recently, more Nippon Steel hot blast furnaces have been built. Germany uses Koppers or Maqin hot blast furnaces; other Western European countries mostly use Dieder hot blast furnaces; in addition to building some external combustion hot blast furnaces, the United States attaches great importance to the transformation of internal combustion hot blast furnaces, which can not only obtain higher blast temperatures, but also extend service life. In recent years, the newly built or rebuilt blast furnace hot blast furnaces in various countries are mainly external combustion type, with air supply temperature of 1200~1350℃, and the dome temperature is generally 1500~1550℃, even close to 1600℃. Therefore, silica bricks are generally used for high-temperature parts of the furnace village and the upper layer of checker bricks, and the use effect is better.

The traditional material of Russian blast furnace hot blast furnace is: the dome and upper masonry are made of high-alumina bricks with an Al2O3 content of 62%~72%, and the middle and lower masonry is made of clay bricks with an Al2O3 content of 38%. Recently, the wind temperature of the hot blast furnace has increased significantly. Therefore, the dome and the upper 6~7m high parts are generally built with low-expansion silica bricks, and the rest of the parts are made of mullite bricks, corundum bricks, kaolin bricks and clay bricks according to different temperatures.

The dome, furnace wall and upper part of the checker bricks of Western European hot blast furnaces are generally built with black silica bricks. Black silica bricks have high iron oxide and titanium oxide contents, high true density, good thermal conductivity, and strong heat storage capacity, so they have high thermal efficiency; the middle and lower furnaces and checker bricks of the hot blast furnace are made of high-alumina bricks and clay bricks respectively. Figure 9-52 is a typical example of refractory materials used in British hot blast furnaces. As can be seen from the figure, the high-temperature parts are all built with silica bricks, the lining and checker bricks of the medium-temperature parts are built with high-alumina bricks, the lining near the hot blast outlet is made of mullite bricks, and the rest of the parts are generally built with clay bricks.

The refractory materials used in German blast furnace hot blast furnaces are silica bricks, sillimanite bricks, mullite bricks, high-alumina bricks and clay bricks from high temperature zone to low temperature zone.
The blast furnace hot blast furnaces in my country are generally internal combustion type, and their linings and checker bricks are generally built with high-alumina bricks and clay bricks; the high-temperature parts of the external combustion hot blast furnaces are generally built with silica bricks, and the medium and low temperature parts are respectively built with high-alumina bricks and clay bricks. In summary, the refractory materials used in blast furnace hot blast furnaces are similar in different countries. However, there is one thing in common, that is, when selecting refractory materials for blast furnace hot blast furnaces, attention must be paid to:
The volume stability of refractory materials;
The high temperature load creep performance of refractory materials;
The thermal expansion performance of refractory materials;
The heat exchange efficiency of hot blast furnaces.
Volume stability of refractory materials. Since the temperature of hot blast furnaces changes frequently and periodically, refractory materials should have good volume stability and uniform thermal expansion to ensure the overall stability of large refractory brick masonry structures.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!