News detail
Monolithic Refractory in glass kilns
In the refractory system of glass kilns, unshaped refractory materials are gradually emerging and playing an increasingly important role. Compared with traditional shaped refractory materials, unshaped refractory materials provide new options for the construction and maintenance of glass kilns with their unique performance and construction advantages.
Definition and characteristics of unshaped refractory materials
Definition: Unshaped refractory materials are a mixture composed of a variety of refractory raw materials and additives. They do not have a fixed shape before use. They need to be formed at the construction site by pouring, ramming, spraying, etc., and they can only have performance after certain curing or baking.
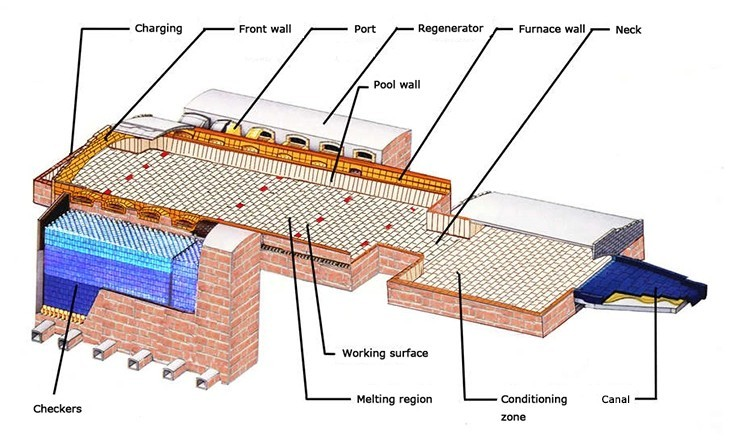
Features
Convenient construction: Unshaped refractory materials can be directly formed at the construction site, without the need for complex masonry work like shaped refractory materials, which greatly shortens the construction period. For example, in the local maintenance of glass kilns, spraying or pouring can quickly complete the repair work and reduce the downtime of the kiln.
Good integrity: After construction, the amorphous refractory can form a whole without obvious joints, which is of great significance for resisting the erosion of high-temperature airflow and glass liquid. In some key parts of glass kilns, such as kiln roofs and flues, amorphous refractory materials with good integrity can effectively avoid damage caused by erosion at joints.
Strong adaptability: Amorphous refractory materials can adjust the raw material formula and the type of additives according to different use requirements and construction conditions, so as to meet the use needs in various complex environments. Whether it is a high temperature zone or a low temperature zone, different corrosive medium environments can find suitable amorphous refractory solutions.
Common types of amorphous refractory materials
Castable: This is the most widely used amorphous refractory material. It is mainly composed of aggregate, powder and binder, and is cast and molded by adding water and stirring. Castables have high strength and good high temperature resistance. Different raw materials can be selected for preparation according to different use temperatures and erosion conditions. Castables are widely used in the bottom and wall of glass kilns.

Ramming material: Ramming material is composed of refractory aggregate, powder and binder. It needs to be compacted by manual or mechanical ramming during construction. Ramming material has high density and corrosion resistance, and is often used in parts of glass kilns that are severely affected by mechanical scouring and high-temperature erosion, such as charging ports and discharge ports.

Spray coating: Spray coating is to spray amorphous refractory materials directly onto the construction site through special spraying equipment. This material has a fast construction speed and can form a uniform coating on the surface of complex shapes. In the maintenance of glass kilns, spray coating can quickly repair damaged parts of the kiln and improve maintenance efficiency.
Application scenarios in glass kilns
Kiln roof application: The kiln roof of the glass kiln is subjected to the radiation and scouring of high-temperature flames, and also needs to have good thermal insulation performance. Castables and spray coatings in amorphous refractory materials can be used for the construction and maintenance of kiln roofs. Castables can form an integral kiln roof structure with good strength and corrosion resistance; spray coatings can form a layer of thermal insulation coating on the surface of the kiln roof to reduce heat loss.
Flue application: Flue is the channel for exhaust gas discharge in glass kilns. The working environment is relatively harsh, with problems such as dust, corrosive gases and temperature fluctuations. Ramming materials and castables in amorphous refractory materials are suitable for flue construction. The high corrosion resistance of ramming materials can resist the erosion of dust and corrosive gases, and the integrity of castables can ensure the sealing of flues.
Application of pool walls and flow holes: Pool walls and flow holes are the parts of glass kilns that directly contact the glass liquid, and the corrosion resistance of refractory materials is extremely high. Some high-performance castables and ramming materials in amorphous refractory materials can be used here. By optimizing the raw material formula and construction process, these amorphous refractory materials can meet the use requirements of pool walls and flow holes to a certain extent.
Construction methods and precautions
Construction methods
Casting construction: First, build the mold according to the design requirements, then pour the evenly stirred castable into the mold, vibrate it and compact it through tools such as vibrating rods to expel the bubbles inside. During the pouring process, pay attention to controlling the pouring speed and height to ensure the pouring quality.
Ramming construction: Lay the ramming material in layers on the construction site, and then use ramming tools to ram it to reach the specified density. Pay attention to uniform force when ramming to avoid local looseness or over-density.
Spraying construction: Load the spray material into the spraying equipment, adjust the spraying pressure and angle, and then spray it evenly onto the construction surface. During the spraying process, pay attention to controlling the spraying thickness and uniformity to avoid leaking or accumulation.
Precautions
Raw material quality control: The raw material quality of amorphous refractory materials directly affects their performance. Therefore, the quality of the raw materials must be strictly checked before construction to ensure that they meet the requirements.
Construction environment control: The temperature, humidity and other conditions of the construction environment have a great impact on the construction quality of amorphous refractory materials. Generally speaking, the construction temperature should be controlled between 5℃ – 35℃, and the humidity should not be too high.
Curing and baking: After the construction is completed, the amorphous refractory materials need to be properly cured and baked. Curing can gradually increase its strength, and baking can remove the moisture in it to avoid damage to the material due to rapid evaporation of moisture during use.
Development trend
High performance: With the continuous development of glass kiln technology, the performance requirements for amorphous refractory materials are getting higher and higher. In the future, amorphous refractory materials will develop towards higher refractoriness, better corrosion resistance and thermal shock stability.
Environmental protection and energy saving: Under the background of increasingly stringent environmental protection requirements, the production and use of amorphous refractory materials will pay more attention to environmental protection and energy saving. R&D personnel will focus on developing new environmentally friendly raw materials and energy-saving construction processes to reduce the impact on the environment.
Intelligent construction: With the advancement of science and technology, the construction of amorphous refractory materials will develop in the direction of intelligence. For example, the use of automated construction equipment and monitoring systems can improve construction quality and efficiency and reduce labor costs.
In short, amorphous refractory materials have broad application prospects in glass kilns. Through continuous technological innovation and performance improvement, amorphous refractory materials will provide stronger support for the development of the glass industry.


Send inquiry
Please Leave your message you want to know! We will respond to your inquiry within 24 hours!